A New Era of Markerless Insect Tracking Technology Has been Unlocked by Retro-ID
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
- Related Works
- Method
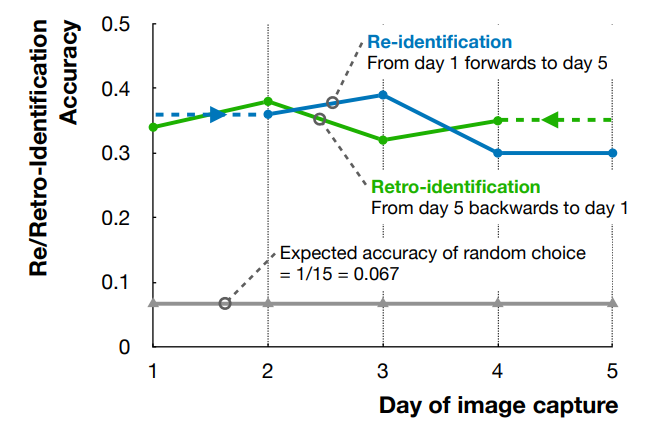
- Results and Discussion
- Conclusion and References
2. Related Works
Explicit recognition of retro-id’s value as distinct from reid, and a need to test its performance are, to the best of our knowledge, novel. Re-id however, is well researched for human faces [12, 13, 19, 20, 24], and somewhat so for insects [2–4, 11, 14–16]. Insect re-id algorithms may rely on small markers or tags attached to an insect to track it over separate observations [2, 4, 14, 15]. Six ant colonies were monitored using tags over 41 days, collecting approximately nine million social interactions to understand their behaviour [14]. BEETag, a tracking system using bar codes, was used for automated honeybee tracking [4], and Boenisch et al. [2] developed a QR-code system for honeybee lifetime tracking. Meyers et al. [15] demonstrated automated honeybee re-id by marking their thoraxes with paint, while demonstrating the potential of markerless reid using their unmarked abdomens. Markerless re-id has been little explored. The study of Giant honeybees’ wing patterns using size-independent characteristics and a selforganising map was a pioneering effort in non-invasive reid [11]. Convolutional neural networks have been used for markerless fruit fly re-id [16] and triplet-loss-based similarity learning approaches have also been used to re-id Bumble bees returning to their nests [3].
\ All these studies adopt chronological re-id despite many highly relevant scenarios where this is inefficient. Our study therefore explores retro-id as a novel complementary approach to tracking individual insects for ecological and biological research.
3. Method
3.1. Data Collection
We obtained reed bees from the Dandenong Ranges National Park, Victoria, Australia (lat. -37.90, long. 145.37)[1]. These bees exhibit semi-social behaviour and construct their nests within the pithy stems of fern fronds and other plants [5]. Each nest can consist of several females who share brood-rearing and defence responsibilities. We placed each insect in a separate container to facilitate individual id for testing. In order to run the experiment over several days, insects were refrigerated overnight below 4°C. After warming up, each bee was individually recorded daily in an arena. Here it was illuminated by an overhead ring light and videoed using a Dino-Lite digital microscope for 30–50 seconds per session at 30 fps. We followed the process listed below to create our final datasets.
\
-
Video Processing: Bee videos were processed frame by frame. To automate this, we trained a YOLO-v8 model to detect a bee’s entire body, head, and abdomen in each frame. This enabled automatic establishment of the bee’s orientation in the frame.
\
-
Image Preparation: Upon detection, bees were cropped from the frames using the coordinates provided by Step 1To align bees, we rotated frames using a bee’s orientation before cropping. Centred on the detected entire bee body, a 400x400 pixel region (determined empirically for our bee/microscope setup) was cropped, then resized to 256x256.
\
-
Contrast Adjustment: To enhance image quality and ensure uniform visibility across all samples, Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalisation (CLAHE) [18] was applied.
\
-
Quality Control: Manual inspection to remove misidentified objects maintained dataset integrity and ensured only bee images were included.
\
-
Dataset Segregation: The final dataset was divided into image subsets, each from a single session, to avoid temporal data leakage.
\ Using Steps 1–5, we curated a dataset of daily bee recording sessions across five consecutive days. Each session included the same 15 individuals videoed for approximately 1200 images/session (total dataset approximately 90K images).
3.2. Network Architecture, Training, Evaluation
We used a transfer-learning-based approach for re-/retro-id of the reed bees. All models were pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset [6] and subsequently fine-tuned using our own dataset. To identify suitable transfer-learning models, we selected 17 different models distributed across 10 different model architectures and parameter numbers ranging from 49.7 million in swinv2s to 0.73 million parameters in squeezenet1_0. To evaluate the models, we collected a second set of data on Day 5, “set-2”, four hours from the first set using Steps 1–5 (above). We trained all 17 models on the first set of Day 5 data. The 17 models were then evaluated based on their ability to re-id individuals in Day 5 set2 data. From them, we selected the seven models with the highest Accuracy (and F1) scores for further consideration. We then trained this top-7 on our original Day 1 and Day 5 data. We evaluated Day 1 models forward on Day 2–5 data and Day 5 models back in time on Day 4–1 data to conduct our main experiments. These forward and backwards evaluations allowed comparison of markerless re- and retro- id of individual insects. The training process was similar for all of the models we considered. We have used Adam Optimiser with a learning rate of 0.001 with 0.0001 weight decay, with a total 100 epochs on the training dataset. We used cross-entropy loss as the loss function for these models.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Asaduz Zaman, Dept. of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University, Australia (asaduzzaman@monash.edu);
(2) Vanessa Kellermann, Dept. of Environment and Genetics, School of Agriculture, Biomedicine, and Environment, La Trobe University, Australia (v.kellermann@latrobe.edu.au);
(3) Alan Dorin, Dept. of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University, Australia (alan.dorin@monash.edu).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

Is Shiba Inu a Good Investment for 2026 After Steep Price Decline?

Cloud mining is gaining popularity around the world. LgMining’s efficient cloud mining platform helps you easily deploy digital assets and lead a new wave of crypto wealth.
